All Categories
Featured
2 people purchase joint annuities, which give a surefire income stream for the rest of their lives. If an annuitant dies throughout the distribution duration, the remaining funds in the annuity might be handed down to a designated beneficiary. The details choices and tax implications will depend upon the annuity contract terms and appropriate regulations. When an annuitant dies, the rate of interest gained on the annuity is handled in different ways depending on the kind of annuity. With a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the passion proceeds to be paid out to the surviving beneficiaries. A fatality benefit is a feature that makes certain a payout to the annuitant's beneficiary if they pass away before the annuity settlements are tired. The accessibility and terms of the death advantage might differ depending on the particular annuity agreement. A kind of annuity that quits all settlements upon the annuitant's death is a life-only annuity. Recognizing the terms and problems of the survivor benefit before buying a variable annuity. Annuities undergo tax obligations upon the annuitant's fatality. The tax treatment depends on whether the annuity is kept in a certified or non-qualified account. The funds undergo earnings tax obligation in a qualified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity commonly causes tax only on the gains, not the whole quantity.
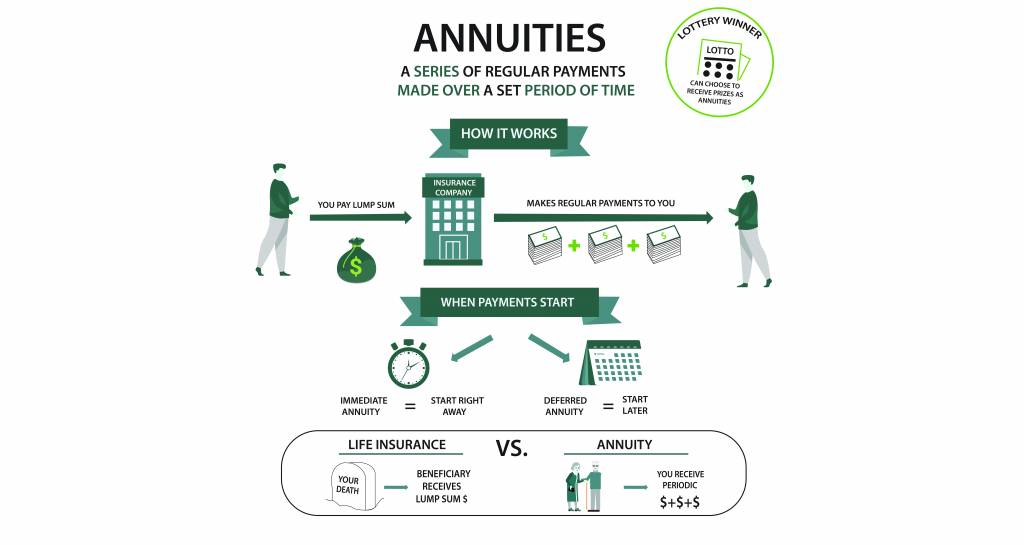
If an annuity's assigned recipient dies, the end result depends on the particular terms of the annuity contract. If no such recipients are assigned or if they, also
have passed away, the annuity's benefits typically revert to the annuity owner's proprietor. If a beneficiary is not named for annuity advantages, the annuity proceeds typically go to the annuitant's estate. Fixed annuities.
Tax implications of inheriting a Flexible Premium Annuities

Whatever section of the annuity's principal was not already exhausted and any incomes the annuity gathered are taxable as revenue for the recipient. If you inherit a non-qualified annuity, you will just owe tax obligations on the incomes of the annuity, not the principal made use of to purchase it. Because you're getting the whole annuity at once, you must pay tax obligations on the entire annuity in that tax obligation year.
Latest Posts
Analyzing Strategic Retirement Planning A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices What Is the Best Retirement Option? Pros and Cons of Variable Vs Fixed Annuity Why Choosing the Right Financial Stra
Understanding Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Income Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Advantages and Disadvant
Decoding Fixed Index Annuity Vs Variable Annuity A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices Breaking Down the Basics of Fixed Annuity Vs Equity-linked Variable Annuity Features of Fixed Annuity Or Va
More
Latest Posts